This section contains articles and important definitions for credit management, credit risk management, credit scoring, credit ratings, collections management and accounts receivable management.

Articles
Important Definitions
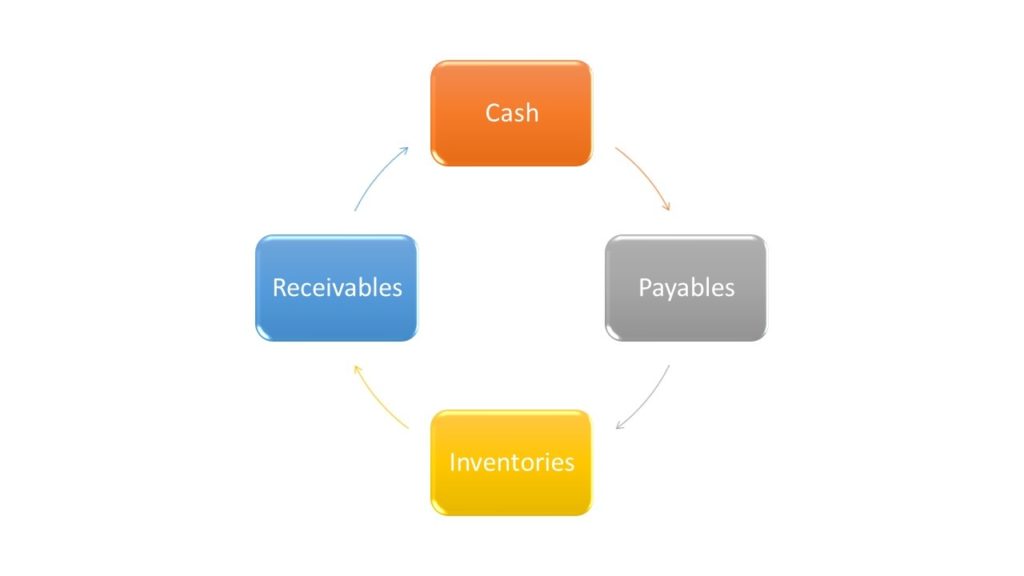
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
The cash conversion cycle (CCC) attempts to measure the length of time each net input dollar is tied up in the production and sales process before it is converted into cash through sales to customers and showing up as cash flows from operating activities.
This metric looks at the length of time needed
- to sell inventory (DSI – Days Sales Inventory),
- to collect receivables (DSO – Days Sales Outstanding) and
- the company is afforded to pay its bills without incurring penalties (DPO – Days Payables Outstanding)
CCC = DSI + DSO – DPO ← min!
under the upper goal to max profit!
CCC measurements usually are based on 30, 90 or 360 days base periods depending on measuring needs and cyclicality of the business.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Collections Management
Collections Management systematically coordinates and executes all required tasks to ensure that liability obligations assigned with the borrower are paid in time.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Code of Ethics
Credit management benefits from a code of ethics describing or defining professional conduct. One such code of ethics is shown below:
- Justice, equity, and confidence constitute the foundation of credit administration.
- Agreements and contracts reflect integrity and should never be breached by either party.
- The interchange of credit information must be based upon confidence, cooperation, reciprocity and confidentiality.
- It is deemed unethical to be a party to unwarranted assignments or transfers of an insolvent debtor’s assets, nor should creditors participate in secret agreements.
- Creditors should cooperate for the benefit of all in adjustment or liquidation or insolvent estates or companies.
- Creditors must render all possible assistance to honest debtors who become insolvent.
- Dishonest debtors must be exposed and referred to the authorities.8. Cooperation, fairness, and honesty must dominate in all insolvent debtor proceedings.9. Costly administrative procedures in the rehabilitation or liquidation of an insolvent debtor shall be avoided at all times.10. Members pledge themselves to uphold the integrity, dignity, and honor of the credit professional in all their business dealings.
Confidentiality Agreement
Confidentiality Agreements are legal binding promises that the receiver of confidential information will not disclose it. Confidential information can be financial statements of a company, that is not obliged to publish those. The customer (borrower) might be willing to disclose financial statements to the borrower’s credit department in order to provide evidence that credit risk is limited and therefore cause a reasonable credit limit.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Assessment
Credit Assessment is the systematic way of analyzing the likelihood of loss arising from credit exposure of a borrower. For this reason, there are several analyzing tools used like
- Credit Scoring Models,
- Robo-advisors (e.g. Emerald Rating),
- Ratings (e.g. Moody’s, Fitch, S&P, D&B, Creditreform) and/ or
- Public credit assessment databases (e.g. Betreibungsamt, Schufa).
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Block
Credit Blocks are usually an exceptional process using credit order control parameters to block customer orders, which fail credit check. It is the authority of an effective credit department to release credit blocked orders only, if the reason for the block is not in place anymore.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit File
Credit files or also called Customer Credit Files should be maintained for every borrower in order to document results of the credit decision that was made during the credit assessment. This is a Sarbanes-Oxley requirement for publicly traded corporations.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Limit
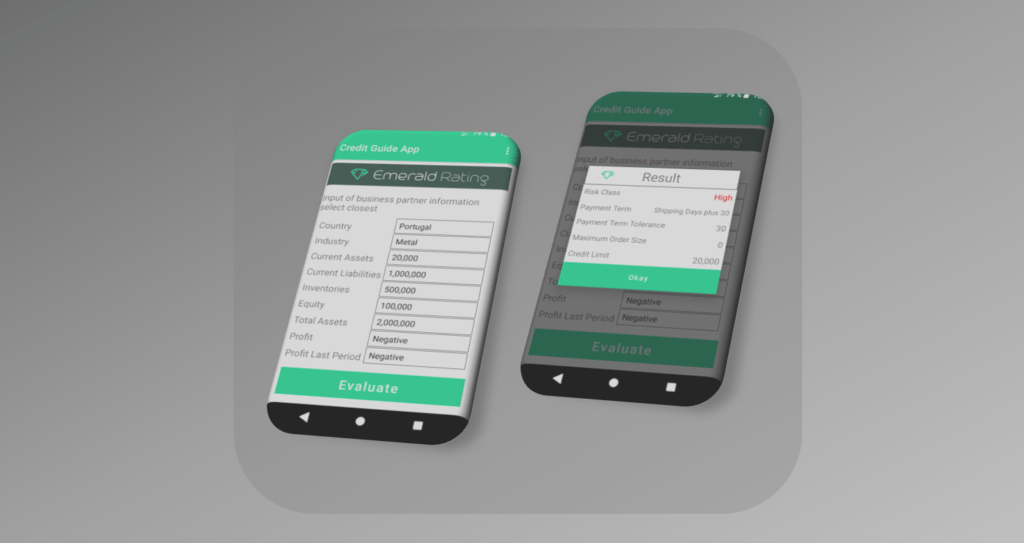
Credit Limit is the authorized maximum amount of credit exposure that has been approved by Credit Management. Credit exposure includes all open accounts receivables and open orders, which are due to be shipped within a defined time window.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Management
Credit Management according to minimum requirements of Credit Management systematically describes the company’s credit exposure with liability obligations assigned with the lender. It consists of Credit Risk Management and Collections Management.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Order Control
It is the responsibility of Credit Management to evaluate customers based on their credit risk and subsequently define credit order control parameters in the company’s ERP system for each customer. These parameters define if a customer order receives a credit blocked or credit warning in the event if credit limit is exceeded and/ or invoices are past due for more than a defined number of days. It is the authority of Credit Management only to release blocked orders.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Rating
A credit rating evaluates the credit worthiness of a debtor, especially a business (company) or a government. It is an evaluation made by a credit rating agency of the debtor’s ability to pay back the debt and the likelihood of default.
Credit ratings are determined by credit ratings agencies. The credit rating represents the credit rating agency’s evaluation of qualitative and quantitative information for a company or government; including non-public information obtained by the credit rating agencies analysts.
Credit ratings are not based on mathematical formulas. Instead, credit rating agencies use their judgment and experience in determining what public and private information should be considered in giving a rating to a particular company or government. The credit rating is used by individuals and entities that purchase the bonds issued by companies and governments to determine the likelihood that the government will pay its bond obligations.
A poor credit rating indicates a credit rating agency’s opinion that the company or government has a high risk of defaulting, based on the agency’s analysis of the entity’s history and analysis of long-term economic prospects.
Source: Wikipedia, October 22, 2019, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Credit_rating
Credit Rating Agencies
A credit rating agency (CRA) is a company that assigns credit ratings for issuers of certain types of debt obligations as well as the debt instruments themselves. In some cases, the servicers of the underlying debt are also given ratings.
In most cases, the issuers of securities are companies, special purpose entities, state and local governments, non-profit organizations, or national governments issuing debt-like securities (i.e., bonds) that can be traded on a secondary market. A credit rating for an issuer takes into consideration the issuer’s credit worthiness (i.e., its ability to pay back a loan), and affects the interest rate applied to the particular security being issued.
The value of such security ratings has been widely questioned after the 2007-09 financial crisis. In 2003, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission submitted a report to Congress detailing plans to launch an investigation into the anti-competitive practices of credit rating agencies and issues including conflicts of interest.[1] More recently, ratings downgrades during the European sovereign debt crisis of 2010-11 have drawn criticism from the EU and individual countries.
A company that issues credit scores for individual credit-worthiness is generally called a credit bureau (US) or consumer credit reporting agency (UK).
Source: Wikipedia, October 22, 2019, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Credit_rating_agency
Credit Review Periods
A Credit Review Period is the time between the last and next credit review. The length usually is defined based upon the credit risk of the customer. Customers should be clustered by risk classes. Credit Review Periods should be defined for every risk class.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Risk
Credit risk is a lender’s risk of loss arising from a borrower who does not fulfill its liability obligations assigned with this lender.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Risk Management
Credit risk management systematically evaluates the overall credit risk to the corporation and mitigates it through
- Limiting Credit Exposure based on credit risk assessments
- Diversifying Customer Portfolio
- Initiating Credit Risk-based Pricing
- Agreeing Covenants- Credit Insurance/ Derivatives
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Credit Risk Management – Code of Best Practice
Purpose of this book is to convey the ability to build up credit risk management in a company and integrate it in its organization. It is used as text book by the Association of Credit Management Switzerland (www.creditmanager.ch) for their educational program.
The author divided this book into chapters addressing
- Standard policy and procedures,
- Standard agreements,
- Key performance indicators for credit risk management,
- Credit risk scoring models and
- Reporting instruments for credit risk management.
These are followed by two chapters about further sources of information and important definitions of credit management.
A differentiation between credit management and credit risk management shall be made at this point. Credit management in a broader sense spans all activities around the analysis and decision-making in regards to credit risk of our customers and the collection of accounts receivables. In this paper the author discusses processes around credit risk, only. He names it credit management in a narrower sense or credit risk management.
Source: Danny Kaltenborn, Credit Risk Management – Code of Best Practice, page 1-2, 2017, https://www.epubli.de/shop/buch/credit-risk-management-code-of-best-practice-danny-kaltenborn-9783745017915/67151

Credit Scoring Models
Credit Scoring Models are weighted key performance measurement systems resulting in a final score with the purpose of validating a borrower’s credit risk. Input variables are based on quantitative and qualitative information. Quantitative information consists of the lender’s balance sheets, income statements and cash flow statements. Qualitative information includes information about legal structure, size of borrower, years present at the market, years of business relationship, educational and experience level of the borrower’s management, geographic diversification, market diversification, payment behavior and the availability of cash, cash-like and credit facilities (i.e. revolving credit line). Credit Scoring Models can further be used to modify the population of final scores based upon economic, geographic and market risk factors using regression analysis. (Also see Robo-Advisor)
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Days Sales Outstanding is an accountancy measure that returns the average time needed to collect accounts receivables from borrowers. It is an efficiency measure of the company’s collection management if neglecting accounts receivable securitization programs. A 90-days-DSO is calculated as the average of three subsequent end of month accounts receivable amounts divided by the sum of these three months’ invoice amounts and multiplied with 90.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Delegation of Authority
Delegation of Authority to approve credit limits and payment terms needs to be granted to Credit Management only by the Chief Financial Officer of the company. It is preferable cascading down certain levels of authorities through Credit Management organization.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Financial Technology (FinTech)
Financial technology, often shortened to fintech, is the technology and innovation that aims to compete with traditional financial methods in the delivery of financial services.
Source: Wikipedia, February 12, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Financial_technology
Going-Concern-Analysis
Going concern value is the outcome of the going concern analysis. The analysis assumes that the company will remain in business indefinitely. Therefore, it is also called ‘total value’. The value can be much different to, if the company is liquidated, because the company value (good will, value of the brand) is not included usually. If the company generates losses over more than one period the going-concern-value will turn negative. Worst scenario is the liquidation by an insolvency/ bankruptcy administrator.
Minimum Requirements of Credit Management
The minimum requirements of Credit Management are published by the Association of Credit Management Switzerland (www.creditmanager.ch) for Switzerland, but is not limiting it by country. It describes how the credit and collections process needs to be defined in a company at the minimum, to ensure credit risk is reasonably mitigated.
Pay Habits/ Payment History
Pay Habits or Payment History is an important tool for Credit Management evaluating credit risk. There can be many reasons why customers pay late. It is important to understand pattern. One-off late payments are usually caused by human errors, which do not potentially raise red flags to the credit manager. More important is to look at customers who chronically pay late. This can be caused by different understandings of the contractual agreement between the two parties and need to be addressed. Or it is a borrower’s cash flow issue, which can result in revoking credit limit. Also, fluctuations in pay habits can be a signal of a cash flow issue. In this case the borrower tries to serve the timely payments to different lenders and does an allocation on a is-more-critical basis.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Payment Terms
Payment Terms is the agreement between borrower and lender about the time, place and method of payments.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Risk Class
Risk Class is one of the output parameters during the Credit Assessment and expresses the customer’s credit risk. Credit Scoring Models can allocate customers to the adequate Risk Class automatically.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Risk Compensation
Risk Compensation covers all legal and financial instruments to minimize damage in case of insolvency of the borrower. Legal instruments are among others the retention of title. It is preferable for processing business to include an extended retention of title in their general terms and conditions. Financial instruments can include bank guarantees, parent guaranties, third-party guaranties and security payments.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/
Robo-advisor
Robo-advisors or robo-advisers are a class of financial advisers that provide financial advice or Investment management online with moderate to minimal human intervention. They provide digital financial advice based on mathematical rules or algorithms. These algorithms are executed by software and thus financial advice do not require a human advisor. The software utilizes its algorithms to automatically allocate, manage and optimize clients’ assets. (Wikipedia, September 19, 2019, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robo-advisor)
Similar to portfolio investment decision making, companies in the B2B arena are faced to making portfolio decisions under risk too. It is about understanding their customer base and associated risk of default for each of them. Adding macroeconomic factors to this equation lets the decision maker gain a better understanding of the risk exposure by industry and country, which the company is exposed to in terms of bad debt risk of its accounts receivable position at the balance sheet. In turn, if there is a mismatch between expectation and reality, corrective action must be initiated.
An example for a digital advisor based on mathematical algorithms is Emerald Rating. It provides a platform for doing pro-active credit risk management for all companies no matter what size, country, and industry.
Sarbanes-Oxley
The Public Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act (Sarbanes-Oxley, SOX) from 2002 requires the CFO and CEO of a publicly traded enterprise to personally certify and attest to the accuracy of their company’s financial statements. This includes accountability, accuracy and integrity of the financial results and requires internal controls over financial reporting (ICFR).
In terms of Credit Management, it is the Bad Debt Reserve process that is ICFR relevant. In order to enable an accountable, accurate and integer reporting of the same all credit decisions have to be documented.
Source: Association of Credit Management Switzerland, October 22, 2019, https://creditmanager.ch/professional-information/